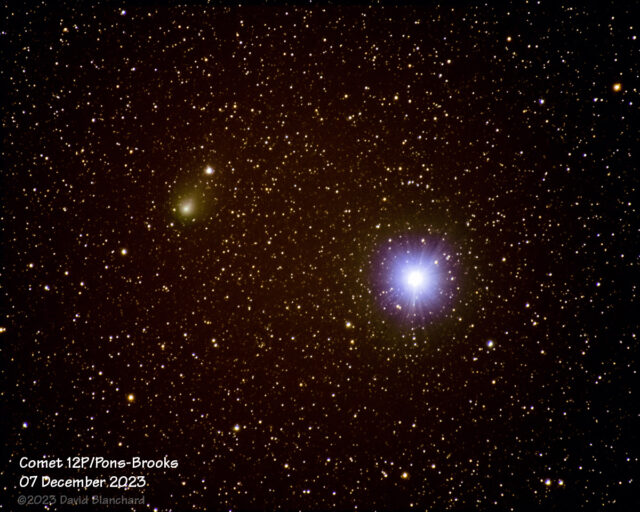
There have been few opportunities for capturing night sky objects owing to clouds and the presence of the Moon. That doesn’t stop me from trying.
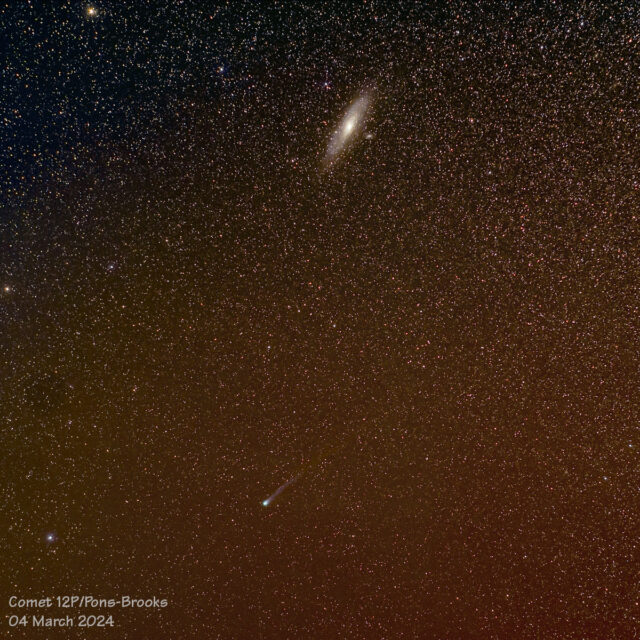
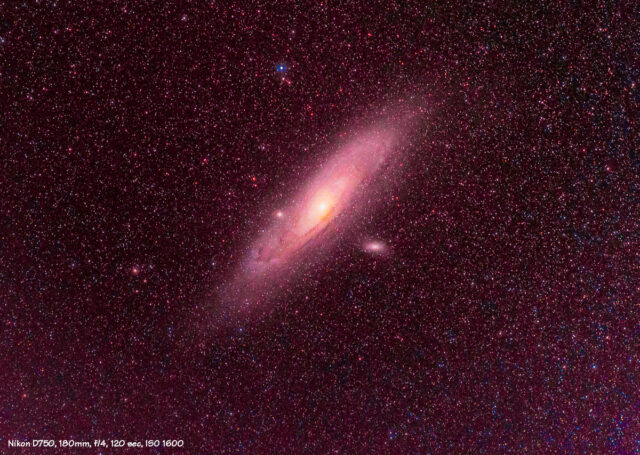
Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks and Triangulum Galaxy (M33).

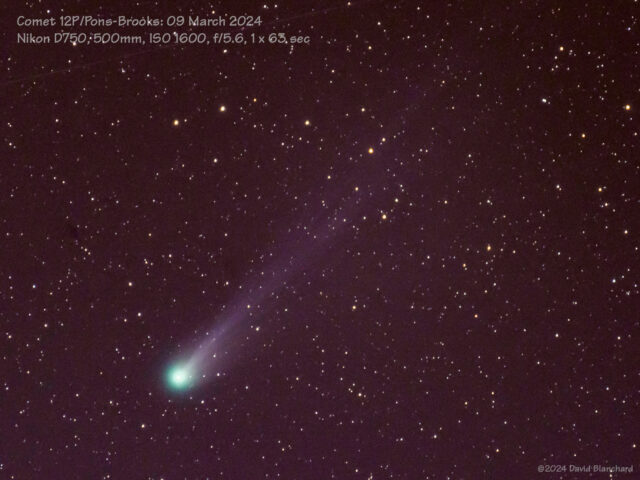
Clouds, a bright waxing Moon, and some distant light pollution made it difficult to capture this comet. This was taken at the base of Arizona Snowbowl ski area at 2830 m; the elevation helps to get above some of the atmospheric haze.
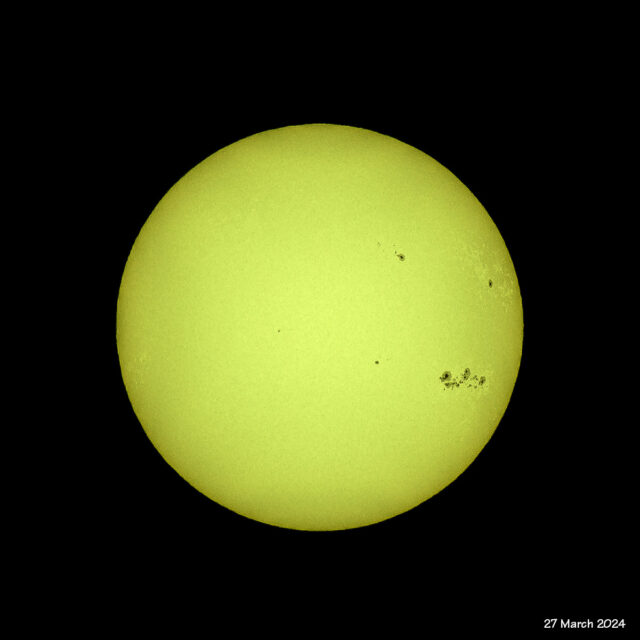
Sunspots AR3615 and AR3614

Zodiacal Light
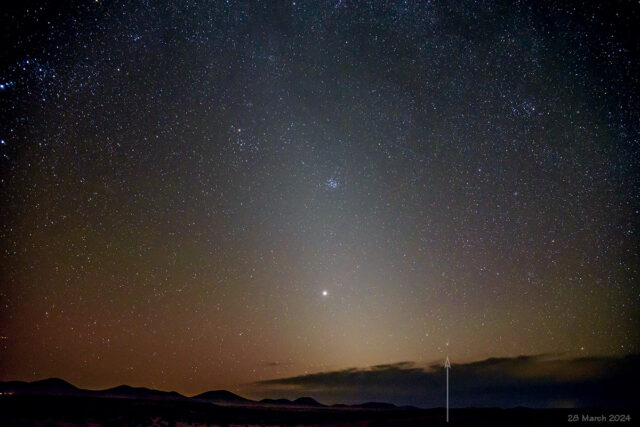

While setting up to photograph a launch at Vandenberg SFB (which was scrubbed), I fired off a few test shots of the zodiacal light. In review, I noticed that I also captured Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks. Small–very small–when shot with a 24mm wide-angle lens.
Now, the Moon is out of the way and the forecast indicates a few clear nights so maybe I’ll get another change to shoot some images of the comet.